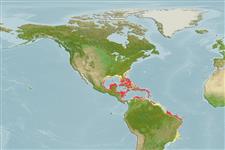
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Écologie
marin récifal; profondeur 1 - 60 m (Ref. 9710), usually 1 - 40 m (Ref. 27115). Tropical; 22°C - 27°C (Ref. 27115)
Western Central Atlantic: Bermuda, Bahamas, and Central America to northern South America.
Length at first maturity / Taille / Poids / Âge
Maturity: Lm ?, range 3 - ? cm
Max length : 8.0 cm TL mâle / non sexé; (Ref. 7251)
Épines dorsales (Total): 12; Rayons mous dorsaux (Total): 10. Bicolored: purple (appearing blue underwater) in front, bight orange-yellow behind (Ref. 26938).
Often found in caves or under ledges. Swim with belly toward substratum, thus under ledges seen upside down. Feed on ectoparasites of other fishes (Ref. 5521). Males show various types of nest care behavior (Ref. 35580). Retreat into recesses when alarmed (Ref. 9710). Have been reared in captivity (Ref. 35420).
Mouthbrooding in this specimen has not been supported by any evidence (Ref. 35580). Prior to spawning, some males established nest sites, using small holes and crevices in the substratum. Females traveled to male nests for egg deposition around dawn. Eggs deposited within the nests were tended by males that established the nests. Males display four types of nest care behaviour: guarding, nest maintenance, detritus clearing,and simple nest entering (Ref. 35580).
Asoh, K. and T. Yoshikawa, 1996. Nesting behavior, male parental care, and embryonic development in the fairy basslet, Gramma loreto. Copeia 1996(1):1-8. (Ref. 35580)
Statut dans la liste rouge de l'IUCN (Ref. 130435)
Menace pour l'homme
Harmless
Utilisations par l'homme
Warning: mysqli::__construct(): (HY000/1040): Too many connections in /var/www/html/includes/func_getlabel.php on line 46
Can't connect to MySQL database (fbapp). Errorcode: Too many connections