Myxini (hagfishes) (hagfishes) >
Myxiniformes (Hagfishes) >
Myxinidae (Hagfishes) > Eptatretinae
Etymology: Eptatretus: hepta (Gr.), seven; tretos (Gr.), perforated (i.e., with holes), referring to seven gill apertures on what would later be described as Homea banksii (=E. cirrhatus) [range within genus is 6-14 pairs of gill apertures]. (See ETYFish); taiwanae: Of Taiwan, off the coasts of which this species occurs. (See ETYFish).
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ekologi
laut dasar (demersal); nir-ruaya; kisaran kedalaman 20 - 50 m (Ref. 31276). Subtropical
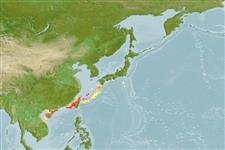
Northwest Pacific: northeastern and southwestern parts of Taiwan.
Size / Weight / umur
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Max length : 33.4 cm TL jantan/; (Ref. 31276)
deskripsi pendek
Morfologi | Morfometrik
Gill apertures usually 6. Slime pores: prebranchial 16-19; branchial 0; trunk 36-42; tail 6-9; total 60-68. Gill apertures nonlinear and crowded.
Copulatory organ absent. The gonads of hagfishes are situated in the peritoneal cavity. The ovary is found in the anterior portion of the gonad, and the testis is found in the posterior part. The animal becomes female if the cranial part of the gonad develops or male if the caudal part undergoes differentiation. If none develops, then the animal becomes sterile. If both anterior and posterior parts develop, then the animal becomes a functional hermaphrodite. However, hermaphroditism being characterised as functional needs to be validated by more reproduction studies (Ref. 51361 ).
Fernholm, B., 1998. Hagfish systematics. p. 33-44. In J.M. Jørgensen, J.P. Lomholt, R.E. Weber and H. Malte (eds.) The biology of hagfishes. Chapman & Hall, London. 578 p. (Ref. 31276)
Status IUCN Red List (Ref. 130435)
Warning: mysqli::__construct(): (08004/1040): Too many connections in /var/www/html/includes/func_getlabel.php on line 46
Can't connect to MySQL database (fbapp). Errorcode: Too many connections